Chipotle Mexican Grill - Research Report - Part 2
Understanding Chipotle's management, numbers and valuation
Welcome to The Dutch Investors, your go-to destination for insightful stock research reports. This week, we're diving deep into Chipotle Mexican Grill. Sign up for free at thedutchinvestors.com to receive weekly reports straight to your inbox. Don't miss out on valuable investment insights!
Chipotle Mexican Grill
This research report is divided into three sections. This is part 2 of 3. In this segment, we will explore:
The management team
Incentives
Skin in the game
Financials
Financial highlights
Debts
KPI’s
The valuation
Ratio’s
Scenario Analysis
4) The management
From grill masters to leaders
Brian Niccol (left) is the CEO of Chipotle. He has been CEO of the company since 2018. Niccol has a long track record in the restaurant industry, having previously worked at Yum! Brands, where he was CEO of Taco Bell, among other things. He came during a difficult period (when Chipotle's brand awareness was seriously damaged) and managed to turn the tide.
John R. Hartung (middle) , 65, has been CFO since 2002. Hartung is a very experienced CFO. He began his career at McDonald's, where he held various management positions for 18 years, including VP and CFO of the Partner Brands Group.
Scott Boatwright, 50, fills the COO position at CMG, where he oversees restaurant operations. Before joining Chipotle, Mr. Boatwright spent 18 years at Arby's Restaurant Group. In his last six years at Arby's, he served as SVP of Operations, where he was responsible for the performance of more than 1,700 Arby's.
4.1 Incentives
“Show me the incentive, and I’ll show you the outcome” - Charlie Munger
Chipotle's management is evaluated (rewarded) based on three performance criteria:
CRS (comparable restaurant growth): The (organic) revenue growth in similar restaurants. Chipotle has a target of 8.8%, but has achieved average growth of 8% in 2022 and 7.9% in 2023.
RCF % (restaurant cashflow percentage ): The percentage of sales converted into restaurant cash flow. Chipotle aims for an RCF percentage of 25% and has achieved an FCF percentage of 23.9% in 2022, just below the target.
SAR (site assessment requests): The number of new potential restaurant locations being considered. Chipotle is targeting 340 SAR per year and has eyed as many as 420 in FY 2022.
Chipotle is clear when it comes to its management team's compensation system. The reward system must be aligned with the interests of shareholders and benefit the company's operations. This includes a compensation plan for management. If you, as an investor, know what the management's 'incentive' is, you most likely also know what management will do (to rake in the bonus) in the near future.
Brian Niccol (CEO) has a base salary of $1.25 million per year. By comparison, the CEO of McDonalds earns $17.7 million annually (as a base salary). The CEO of Darden Restaurant $8.5 million. The CEO of Texas Roadhouse $4.4 million and the CEO of Shake Shack $3.3 million. Niccol also receives LTI (Long Term Incentive) options, which are based on the company's performance. The LTI options are intended to align the interests of the CEO with those of the shareholders. It seems that the CEO receives a relatively low base salary, if you compare it with peers in the sector, which could make the 'incentive' to rake in the bonus even greater.
4.2 Skin in the Game
The CEO is required to have at least 7 times his base salary in shares. The CFO at least 4 times and the other management members at least 3 times the basic salary in shares. This ensures that the interests of management and shareholders are better aligned.
As Nassim Taleb says:
“If you don't have skin in the game, you have no reason to be honest.”
This means that managers who have a financial interest in the company are more likely to make decisions that are in the best interests of the company (and therefore also its shareholders).
Chipotle CEO Brian Niccol owned 76.500 shares worth +/- $183 million in April 2023. This is more than 146 times his base salary.
Chipotle CFO Jack Hartung owns approximately 78.000 shares worth +/- $187 million. This is approximately 220 times his base salary.
Chipotle's COO, Scott Boatwright, owned about 17.000 shares, worth $41 million. This is approximately 48 times his base salary.
It appears to me management has more then enough ‘skin in the game’, so one would assume interest are alligned with shareholders.
5) - Financials
The numbers behind the burritos
5.1 Financial performance
Chipotle Mexican Grill has achieved impressive sales growth over the past decade, with sales increasing from $3.2 billion in FY 2013 to $9.9 billion in FY 2023, with an average annual growth rate of more than 12%. Over the past three years, this growth accelerated to 14%, mainly due to accelerated digitalization during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Cost structure
Chipotle Mexican Grill (CMG) has a cost structure characterized by high labor costs. Labor costs amount to 25% of the total costs, while the purchasing costs of food and drinks are approximately 30%.
The other costs, including rent and other indirect costs, amount to 15%. This cost structure leads to an operating profit margin of 25% per restaurant. However, overhead costs amount to another 10%, making the bottom line operating profit margin +/- 15%. An average CMG restaurant turns over about $3 million per year, which equates to $450,000 in profit per restaurant. (+/- 3700 restaurants x $450.000 per restaurant is $1.7 billion. (Approximately FY 2023 profit).
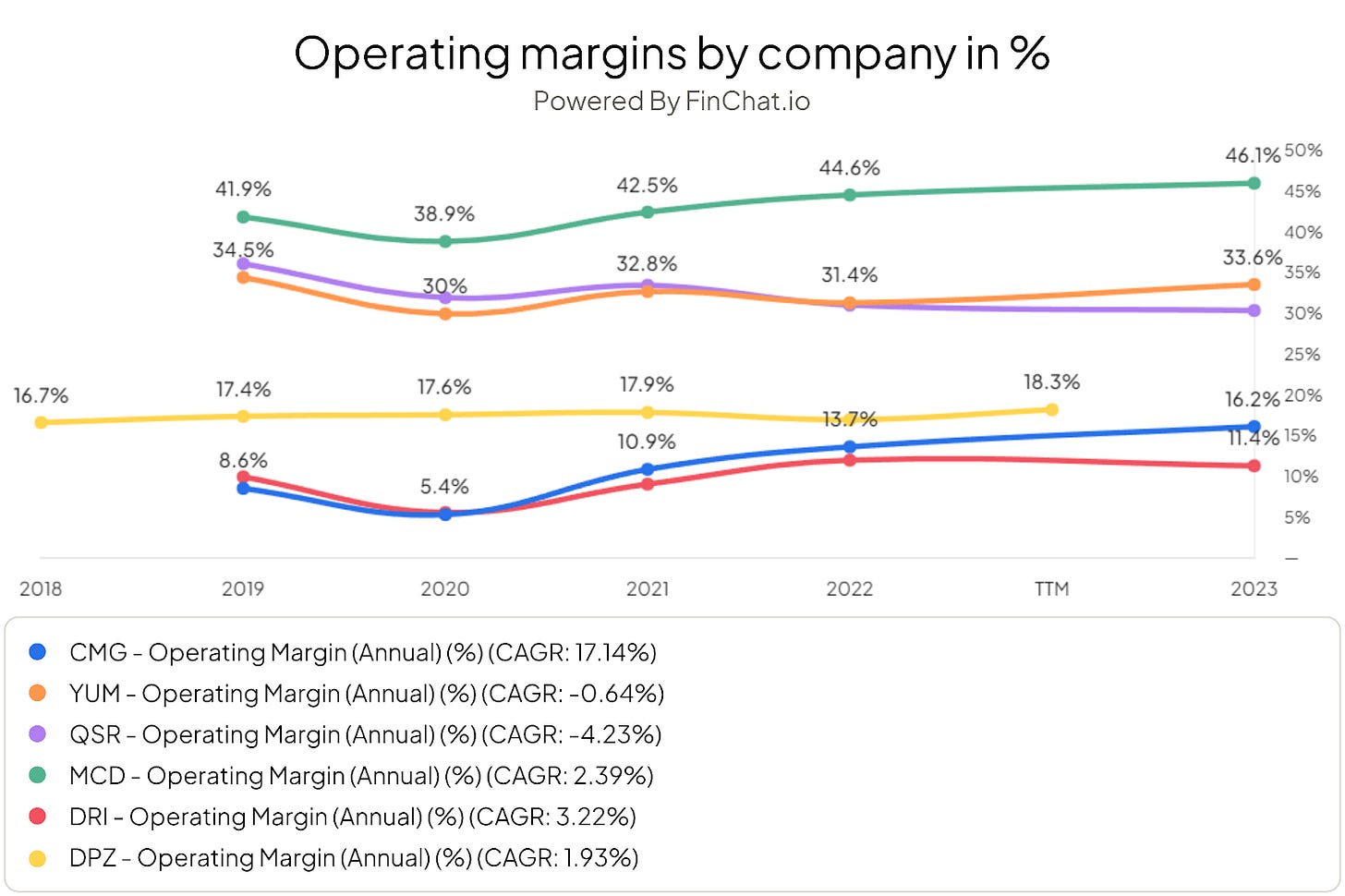
Chipotle currently sits at the bottom of the segment with an operating profit margin of 16.2%, which is significantly lower compared to other restaurant chains. Unlike Chipotle, McDonald's and Yum! Brands have operating margins of 46.1% and 33.6%, respectively. There are a number of factors that can account for the significant difference between Chipotle (CMG) and its rivals.
Companies like McDonald's have the scale and brand recognition to get better prices for their ingredients. Chipotle also likes to ‘own’ its restaurants for more control and consistency, while many other chains use the franchising model.
An important aspect is the cost structure of any company. Chipotle is known for using high-quality and often locally sourced ingredients, which can increase purchasing costs compared to more standardized products from McDonald's and Yum! Brands. The pursuit of premium ingredients not only increases the cost of raw materials, but can also lead to increased complexity in the supply chain. Which in turn can lead to, you guessed it, higher costs.
Another point to consider is labor costs. Chipotle generally charges higher wages for its employees, which puts pressure on margins.
Chipotle and Texas Roadhouse compare quite well. They have a similar market value, operate a similar business model and both have few franchises. Moreover, they emphasize high-quality products and services. Comparing the operating margins of Chipotle and Texas Roadhouse reveals a significant difference. Chipotle's operating profit margin is more than double that of Texas Roadhouse, standing at 8.6% for Texas Roadhouse.
CMG does have the potential to improve its operating profit margin by continuing to grow. If CMG grows, its overhead costs will grow less than the other costs. This is because overhead costs are relatively stable, while other costs increase as the number of restaurants grows. Chipotle’s business model is also more scalable compared to Texas Roadhouse. CMG's high(er) profit margins, combined with a high(er) turnover rate, lead to a surprisingly high ROIC for a growing, fairly capital-intensive company. CMG's ROIC is currently (March 2023) approximately 18%
Chipotle's net profit grew faster than revenue in recent years, increasing from $230 million in 2013 to $1.2 billion in 2023. A growth rate of 36.7% compared to FY 2022.
Net profit growth has actually accelerated over the past three years, thanks to rising operating margins, increasing digital sales, and investments in growth. Over the past decade, Chipotle's earnings per share (EPS) have grown at an average annual rate of nearly 16%.
5.2 Debts
We can be quite brief about Chipotle's debt position. They currently (March 2024) have about $580 million in cash and $4 billion in debt. These 'debts' are mainly leases and offices. As of September 30, 2023, Chipotle had only $500,000 in interest-bearing debt. In the TTM (trailing twelve months), Chipotle has a debt / free cash flow (debt / fcf) ratio of 3.3. This is pretty healthy for the type of company Chipotle is. For comparison: McDonald's (#MCD) scores a 7.2, Restaurant Brands International (#RBI) an 11.5 and Starbucks (#SBUX) 5.5. With a debt / EBITDA ratio of 2, this is also below our threshold value of <3. I don't foresee any problems when it comes to current debts.
5.3 KPI’s
To assess Chipotle's performance, Chipotle monitors four critical indicators (KPIs):
Same-store sales growth;
Operating costs as % of sales;
Number of newly opened restaurants (new restaurant openings);
Online sales as a percentage of turnover (digital orders % of sales).
We'll go through each of these KPIs, discuss their relevance, and see how Chipotle has performed recently.
1 - How much they earn and grow in their existing restaurants (same-store sales)
Same-store sales is an important KPI for Chipotle Mexican Grill because it measure the growth of the company's existing restaurants. High growth in restaurants indicates that Chipotle is successful in attracting new customers and retaining existing customers.
Due to the unexpected Corona pandemic, Chipotle had to quickly respond to the changing climate and implemented digital sales channels and Chipotlanes (drive-throughs) within a few months in order to stay afloat. This strategy has paid off. Digital orders and Chipotlanes are now a significant part of Chipotle's future success. Management is rewarded when same-store sales growth is between 6.8% and 12% per year. With an average growth rate of 9.8% over the past 5 years, this seems quite feasible
2 - How much money they spend on their restaurants as a percentage of turnover (operating costs as % of revenue)
The percentage of sales a company spends on its restaurants is an important KPI, as it provides an indication of the efficiency of its operations. The lower the percentage, the more efficient they are. A higher percentage indicates that the restaurant (may) have inefficiencies or a higher cost structure.
Chipotle Mexican Grill has a relatively high percentage of restaurant operating costs, with an average of 78.5% over the past five years. Chipotle's restaurant operating costs are lower than those of other fast food chains, such as Starbucks (81.2%), McDonald's (80.9%) and Darden Restaurants (78.9%). Taco Bell has one of the lowest operating costs of all fast food chains, at 75.2%. If you are looking for an as profitable as possible' company, you want this percentage to decrease. However, it is important that it does not become 'too' low, which means that salaries will be lower, investments will be lower and savings may be made on quality. Chipotle must find a balance here. I expect an operating margin (as a % of sales) between 75%-78% to be healthy and feasible.
3 - How many new restaurants Chipotle is opening (new restaurant openings)
New restaurant openings are also an important KPI for Chipotle. A high number of new restaurant openings indicates that the company is investing, growing, and exploring new markets. This can lead to increased sales and, ultimately, profitability. In general, management estimates the number of new locations to be lower than they do the following year. This is positive. A good example of; “under promise, over deliver”.
4 - How much Chipotle sells online (digital orders % of sales).
A high percentage of digital orders indicates that the company is successful in reaching customers through digital channels. In 2019, Chipotle's percentage of digital orders was 'only' 18%. This changed dramatically in 2020, when the pandemic increased demand for online ordering. In 2020, digital orders accounted for 46.2% of sales. In the years 2021 and 2022, the percentage of digital orders decreased slightly, but still remained high compared to the previous years. The company aims to ultimately generate 40% of its turnover from digital orders. This seems like an achievable goal to me. In FY 2023, the percentage of digital orders was 37.4% of sales. A slight decrease compared to FY 2022. Digital orders are more profitable then ‘regular’ orders.
Going forward, Chipotle will need to continue to focus on efficiency and growth. The company must ensure that it balances its restaurant operating costs and that it can continue to open new restaurants and drive digital orders. However, the price-quality ratio should not suffer. That's the thread on which Chipotle balances itself.
6) - The valuation
What is the burrito maker worth?
6.1 Ratio’s
Chipotle Mexican Grill is a company that is between a 'young adult' and 'adult' phase. The company is investing heavily in growth by opening new restaurants in the US and internationally. Over the past eight years, earnings per share (EPS) have increased by almost 700%. This is due to a number of factors, including: improved operating margins, increasing digital sales, decreasing outstanding shares, higher efficiency and investing in growth.
Chipotle currently has +/- 3400 restaurants. If they open an average of 200 new restaurants per year, it will have a total of 5,400 restaurants by 2034. This is a CAGR of 4.7%. Chipotle itself indicates that it wants to grow about 8% per year by opening new locations. If we look at the history and what management has shown so far, 8% per year seems feasible. If Chipotle can grow sales 4% per year at their current restaurants, 12% seems feasible over the next 3 years (8% + 4%). We then slowly scale down the growth to 10%. We are slowly scaling down growth because, as you grow as a company, it is difficult to grow. It is also a matter of remaining conservative to build in the safety margin.
6.2 Scenario analysis
From the current share price ($2915), Chipotle doesn't seem like a good investment. Chipotle is very competitively priced at 66 times earnings. Little can go wrong to justify the current valuation. (Updated on April 24th 2024).
Since the scenario analysis, the stock price has increased from $2915 to $3209, which means the expected annual return has decreased even more to -10%. Chipotle seems to be priced to perfection.
Part 3 of 3 is coming soon!
Want our Dutch-written and audio analyses? Click here.